Numpy(Numerical Python) :
- C/ C++/ 포트란 등의 언어와 통합 가능
- 고성능 수치계산에 특화된 라이브러리
- 벡터 및 행렬 연산에 있어서 굉장히 편리한 기능을 제공
- pandas 와 matplotlib 의 기반이 되는 data handling 모듈
- 리스트에 비해 빠르고 메모리 효율적
- 반복문 없이 데이터 배열에 대한 처리를 지원
- 선형대수와 관련된 다양한 기능 제공
*파이썬은 interpreter 언어이기 때문에 처리 속도에 문제가 있는데 이를 보완할 수 있는 모듈
1. numpy 불러오기
import numpy as np보통은 numpy 를 np 라는 명칭(alias) 으로 불러옴
2. np.array : 배열을 행렬로
#np.array
x = [1,2,3,4]
y = np.array(x)
print(y)
##출력
#array([1, 2, 3, 4])#numpy type
type(y) # 출력 : numpy.ndarray#vector
vector = [1,2,3,4,5]
np.array(vector)
#matrix
matrix = [[1,2,3,4],[1,2,3,4],[1,2,3,4]]
np.array(matrix)
#tensor
tensor = [[[1,2,3,4],[1,2,3,4],[1,2,3,4]],
[[1,2,3,4],[1,2,3,4],[1,2,3,4]],
[[1,2,3,4],[1,2,3,4],[1,2,3,4]],
[[1,2,3,4],[1,2,3,4],[1,2,3,4]]]
np.array(tensor)#dtype
np.array([[1,2,3],[4.5,5,6]], dtype = int )
np.array([[1,2,3],[4.5,"5","6"]], dtype = np.float32)#size : shape의 모든 값 곲
np.array(tensor,int).size#ndim
np.array(tensor,int).ndim #출력 : 3
*shape : numpy array 의 dimension 구성을 '튜플' 형태로 반환
*ndim : number of dimension (1 : vector, 2 : matrix, 3 : tensor)
*size : number of data (shape 모든 곱)
*dtype : numpy array의 데이터 타입 설정
3. Handling Shape : reshape/ flatten
#reshape
test_matrix = [[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8]]
np.array(test_matrix).shape # (2, 4)
np.array(test_matrix).reshape(8,) # (8, 1)
np.array(test_matrix).reshape(-1,4) # (2, 4)
np.array(test_matrix).reshape(-1,2) # (4, 2)
np.array(test_matrix).reshape(2,2,2) # (2, 2, 2)#faltten
test_matrix = [[[1,2,3,4],[1,2,5,8]],[[1,2,3,4],[1,2,4,6]]]
np.array(test_matrix).flatten() # (16, )*reshape 에서 -1의 의미 : 원래 shape의 길이와 결정된 reshape 차원가지고 나머지 차원 추정하여 결정
4. indexing and slicing (1dim & 2dim)
indexing : 앞은 row, 뒤는 column 을 의미
slicing : 리스트와 달리 행, 열을 나눠서 슬라이싱 가능, matrix에서 부분집합 추출시 유용
[start, end+1, step]
# 1-dimension array index and slice
y[1] #두 번째 성분
y[1:] #두 번째 성분부터 끝까지
y[:2] #처음부터 두 번째 성분까지
y[-1] #맨 마지막 성분
y[:-1] #맨 마지막에서 두 번째 성분까지# 2-dimension array index and slice
y2[:,:] #행렬 전체
y2[0, 1:3] #첫 행, 두 번째에서 세 번째 열#argmax : max index
a = np.array([1,2,3,4,5,6,6,4,4,3])
np.argmax(a) #5
#argmin : mimn index
a = np.array([1,2,3,4,5,6,6,4,4,3])
np.argmin(a) #0*argmin, argmax : min/max index
5. creation array : linspace(start, end, count), arange(n)
#linspace 수열 생성
np.linspace(0,10,101)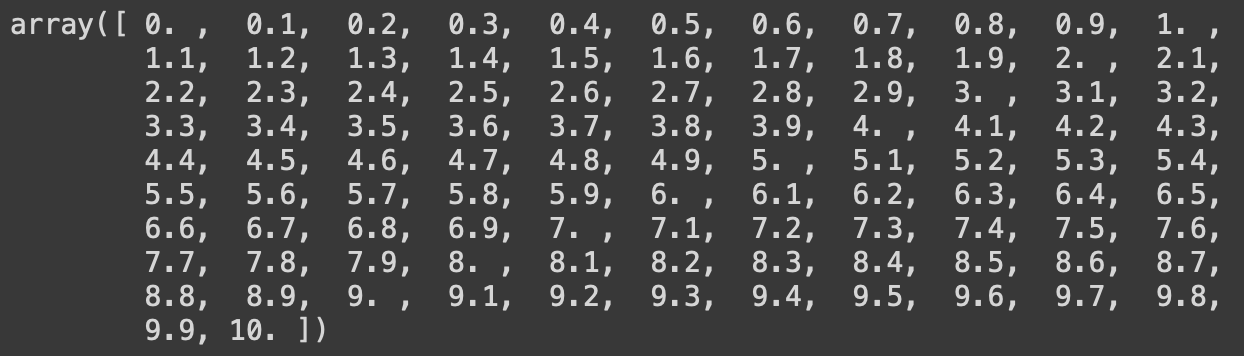
0부터 10까지 101개의 데이터 생성
#arange(n) : n개의 숫자 배열 생성
np.arange(30).reshape(5,6)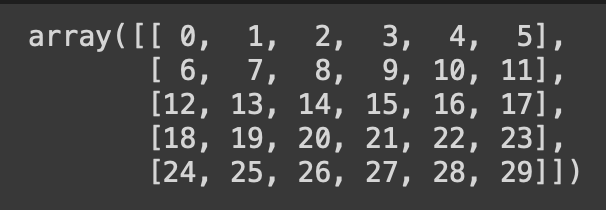
30까지의 배열을 (5, 6) shape 으로 형성
6. creation function : empty, something _like, identity, eye, diagonal
#empty
np.empty(shape = (10,), dtype = int) #shape 에 맞는 아무 행렬 형성
#something_like
test_matrix = np.arange(100).reshape(5,-1) #기준 matrix
np.ones_like(test_matrix) #위 shape 에 맞는 ones matrix
np.zeros_like(test_matrix) #위 shape 에 맞는 zeros matrix
np.empty_like(test_matrix, dtype = float) #위 shape 에 맞는 empty matrix
#identity
np.identity(n = 3, dtype = int) #(n, n) shape
#eye(N, M, k)
#N : 행 사이즈
#M : 열 사이즈
#k : 1이 시작되는 column index
np.eye(N = 3, M = 5, dtype = int) #(N, M) shape
np.eye(N = 3, M = 5, k =2, dtype = int)
#diagonal : 대각성분
matrix = np.arange(9).reshape(3,3)
np.diag(matrix)
np.diag(matrix, k = 2)
7. random sampling : random.uniform, random.normal
#uniform
np.random.uniform(0,1,10).reshape(2,5)
#normal : loc = 0.0, scale = 1.0, size = None
np.random.normal(0,1,10).reshape(2,5)

8. array calculation1 : summation, mean, std, min, max
#multi dimension array
y2 = np.array([[1,2,3,4], [5,6,7,8]])
print(y2.shape) #2*4 size
y3 = np.array([[1,2],[3,4]])
print(y3.shape) #2*2 size#summation and mean
np.sum(y2) #all summation
np.sum(y2, axis = 0) #column summation
np.sum(y2, axis = 1) #index summation
np.mean(y2) #all mean
np.mean(y2, axis = 0) #column mean
np.mean(y2, axis = 1) #index mean
np.std(y2) #all std
np.std(y2, axis = 0) #column std
np.std(y2, axis = 1) #index std
np.max(y2) #maximum
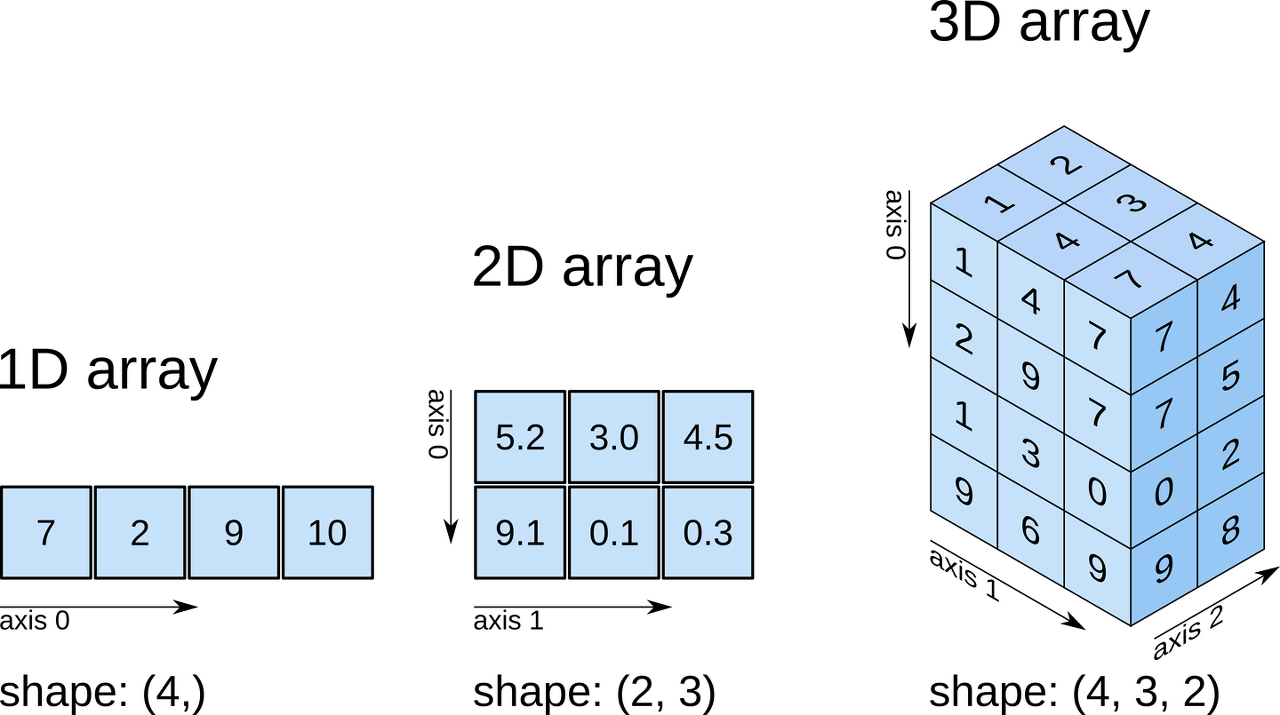
np.min(y2) #minimum*axis
[2-dimension]
axis = 0 : column
axis = 1 : index
[3-dimension]
axis = 0 : layer
axis = 1 : index
axis = 2 : column
9. array calculation2 : exponential, squart, h/vstack, concatenate
#exponential : 각 성분 모두 exponential
test_array = np.arange(1,13).reshape(3,4)
np.exp(test_array)
#squart : 각 성분 모두 제곱근
test_array = np.arange(1,13).reshape(3,4)
np.sqrt(test_array)#hstack : horizontal stack
a = np.array([1,2,3])
b = np.array([2,3,4])
np.hstack((a,b))
#vstack : vertical stack
a = np.array([1,2,3])
b = np.array([2,3,4])
np.vstack((a,b))#concatenate
a = np.array([[1],[2],[3]])
b = np.array([[2],[3],[4]])
np.concatenate((a,b),axis = 0) #hstack
np.concatenate((a,b),axis = 1) #vstack
10. array calculation3 : dot_product, transpose, etc.
#dot_product
test_a = np.arange(1,7).reshape(2,3)
test_b = np.arange(7,13).reshape(3,2)
test_a, test_b
#or
test_a.dot(test_b) #(2,3)*(3,2)
#or
test_a@test_b
#or
np.matmul(test_a, test_b)#transpose
a = np.arange(1,7).reshape(2,3)
a.transpose()
a.T
11. scalar-vector-matrix calculation
#matrix and scalar
test_matrix = np.array([[1,2,3],[3,4,5]],int)
scalar = 3
test_matrix + scalar #모든성분에 3 합
test_matrix/scalar #나누기
test_matrix//scalar #몫
test_matrix&scalar #나머지
test_matrix**scalar #n제곱#vector-matrix
matrix = np.arange(1,13).reshape(4,3)
vector = np.arange(10,40,10) #[[10,40,10],[10,40,10],[10,40,10]]
matrix + vector #addition
matrix - vector #subtraction
matrix * vector #product
12. numpy performance
# time comparison : for vs. list vs. numpy
def sclar_vector_product(scalar, vector) :
result = []
for value in vector :
result.append(scalar*value)
return result
iteration_max = 1000000
vector = list(range(iteration_max))
scalar = 2
%timeit sclar_vector_product(scalar,vector) #for loop 성능
%timeit [scalar*value for value in range(iteration_max)] #list pythonic 성능
%timeit np.arange(iteration_max)*scalar #numpy 성능*timeit : 계산 속도 도출
일반적으로 속도는 for loop < list comprehension < numpy
13. comparison : all & any, logical_and, logical_or, isnan, isfinite
#all and any
a = np.arange(10)
np.all(a>5) #False
np.any(a>5) #True#logical_and
a = np.array([1,3,0[], float)
np.logical_and(a>0, a<3) #True, False, False#logical_or
b = np.array([True, True, False], bool)
c = np.array([False, True, False],bool)
np.logical_or(b,c) #array([ True, True, False])#isnan
a = np.array([1, np.NaN, np.Inf], float)
np.isnan(a) #array([False, True, False])#isfinite
a = np.array([1, np.NaN, np.Inf], float)
np.isfinite(a) #array([ True, False, False])
'Python > Data Analysis' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 데이터 시각화_matplotlib(1) - plt 기본 설정 (0) | 2023.05.21 |
|---|---|
| Pandas(DataFrame) (0) | 2023.05.16 |

