728x90
Linear Regression (선형회귀) : 데이터들을 가장 잘 표현하는 직선의 방정식을 찾는 것
Data 를 대표하는 hypothesis를 직선의 방정식으로 설정
y = W1x1 W2x2 + B
Step1) Hypothesis

Step2) Cost function

Step3) Training - gradient descent method


Numpy
w/ min-max scaling
#load module
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
#input & label (age/BMI and blood pressure)
x_input = np.array([[25,22],[25,26],[25,30],[35,22],[35,26],[35,30],[45,22],[45,26],[45,30],
[55,22],[55,26],[55,30],[65,22],[65,26],[65,30],[73,22],[73,26],[73,30]], dtype= np.float32)
labels = np.array([[118],[125],[130],[118],[126],[123],[120],[124],[130],[122],[125],[130],
[127],[130],[130],[125.5],[130],[138]], dtype= np.float32)
#weight and bias
W = np.random.normal(size=(2, 1))
B = np.random.normal(size=())
#min-max scaling
x_input_org = x_input
xmin, xmax = np.min(x_input, axis = 0), np.max(x_input, axis = 0)
x_input = (x_input - xmin)/(xmax-xmin)
#Function Generation
def Hypothesis(x) :
return np.matmul(x,W)+B
def Cost() :
return np.mean((Hypothesis(x_input)- labels)**2)
def Gradient(x,y):
global W, B
delta = 5e-7
#W gradient
pres_W = W.copy()
grad_W = np.zeros_like(W)
for i in range(W.size):
W[i,0] = pres_W[i,0] + delta
cost_p = Cost()
W[i,0] = pres_W[i,0] - delta
cost_m = Cost()
grad_W[i,0] = (cost_p - cost_m)/(2*delta)
W[i,0] = pres_W[i,0]
#B gradient
pres_b = B
B = pres_b + delta
cost_p = Cost()
B = pres_b - delta
cost_m = Cost()
grad_B = (cost_p-cost_m)/(2*delta)
B = pres_b
return grad_W, grad_B
def Predict(x):
return Hypothesis((x-xmin)/(xmax-xmin))
#Parameter
epochs = 1000
lr = 0.05
training_idx = np.arange(0, epochs+1, 1)
cost_graph = np.zeros(epochs+1)
#Training
for cnt in range(0, epochs + 1):
cost_graph[cnt] = Cost()
if cnt%(epochs//20) == 0:
print("[{:>7}] Cost = {:>10.4}, W = [[{:>7.4}] [{:>7.4}]], B = {:>7.4}".format(cnt, Cost(), W[0,0], W[1,0],B))
grad_W, grad_B = Gradient(x_input, labels)
W -= lr * grad_W
B -= lr * grad_B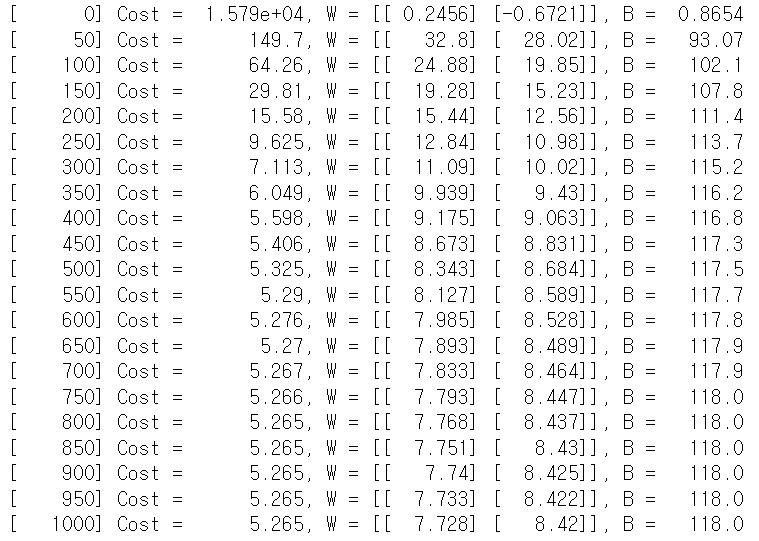
#Prediction
age = 29.0
BMI = 25.0
print("Age - {}, BMI - {} : {}mmHg".format(age, BMI, Predict([age, BMI])))
Age - 29.0, BMI - 25.0 : [121.81400206]mmHg
#Cost function graph
plt.title("'Cost / Epochs' Graph")
plt.xlabel("Epochs")
plt.ylabel("Cost")
plt.plot(training_idx, cost_graph)
plt.xlim(0, epochs)
plt.grid(True)
plt.semilogy()
plt.show()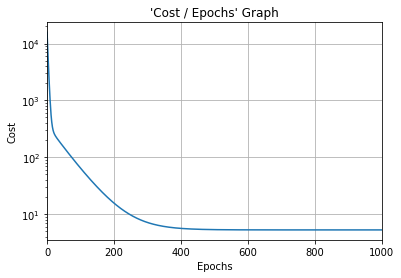
#for surface
x_range = np.arange(0,1,0.01)
y_range = np.arange(0,1,0.01)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x_range, y_range)
Z = X*W[0,0] + Y*W[1,0] + B
#plotting
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111,projection = '3d')
ax.scatter(x_input[:,0], x_input[:,1], labels, c = 'red', marker = 'o', alpha = 0.5)
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, alpha = 0.5)
ax.set_xlabel('scaled Age')
ax.set_ylabel('scaled BMI')
ax.set_zlabel('Blood Pressure')
plt.title('Data and Regression surface')
plt.show()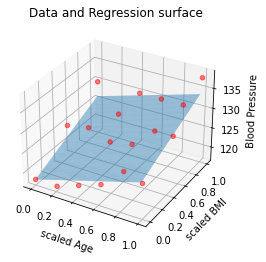
Tensorflow
w/ min-max scaling
#load module
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
#input & label (age/BMI and blood pressure)
x_input = tf.constant([[25,22],[25,26],[25,30],[35,22],[35,26],[35,30],[45,22],[45,26],[45,30],
[55,22],[55,26],[55,30],[65,22],[65,26],[65,30],[73,22],[73,26],[73,30]], dtype= tf.float32)
labels = tf.constant([[118],[125],[130],[118],[126],[123],[120],[124],[130],[122],[125],[130],
[127],[130],[130],[125.5],[130],[138]], dtype= tf.float32)
#weight and bias
W = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal((2, 1)), dtype=tf.float32)
B = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal(()), dtype=tf.float32)
#min-max scaling
x_input_org = x_input
xmin, xmax = np.min(x_input, axis = 0), np.max(x_input, axis = 0)
x_input = (x_input - xmin)/(xmax-xmin)
#Function Generation
def Hypothesis(x) :
return tf.matmul(x,W) + B
def Cost() :
return tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(Hypothesis(x_input)-labels))
def Predict(x):
return Hypothesis((x-xmin)/(xmax-xmin))
#Parameter
epochs = 5000
lr = 0.01
opt = tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(learning_rate=lr)
training_idx = np.arange(0, epochs+1, 1)
cost_graph = np.zeros(epochs+1)
#Training
for cnt in range(0, epochs+1):
cost_graph[cnt] = Cost()
if cnt % (epochs//20) == 0:
print("[{:>6}] cost = {:>10.4}, W = [ {:>7.4} {:>7.4} ], B = {:>7.4}".format(cnt, cost_graph[cnt], W[0,0], W[1,0], B.numpy()))
opt.minimize(Cost,[W, B])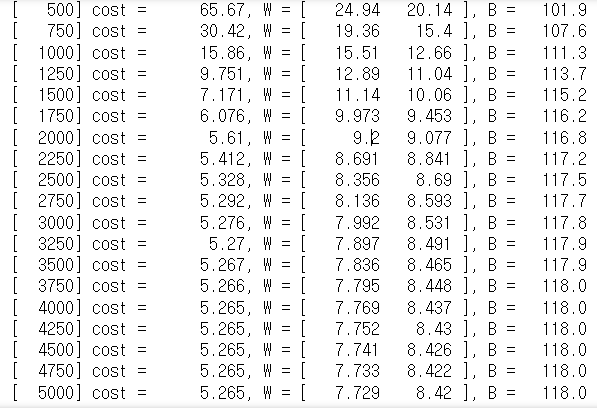
#Validation Test
H_x = Hypothesis(x_input)
for x,h,l in zip(x_input_org, H_x, labels):
print("Age : {}, BMI : {:>7.4} => BP : {:>7.4} [label => {}]".format(x[0],x[1],h[0],l))
#Prediction
age = 29.0
BMI = 25.0
test = tf.constant([[age,BMI]], dtype = tf.float32)
print("Age - {}, BMI - {} : {}mmHg".format(age, BMI, Predict(test)))
Age - 29.0, BMI - 25.0 : [[121.81373]]mmHg
#Cost function graph
plt.title("'Cost / Epochs' Graph")
plt.xlabel("Epochs")
plt.ylabel("Cost")
plt.plot(training_idx, cost_graph)
plt.xlim(0, epochs)
plt.grid(True)
plt.semilogy()
plt.show()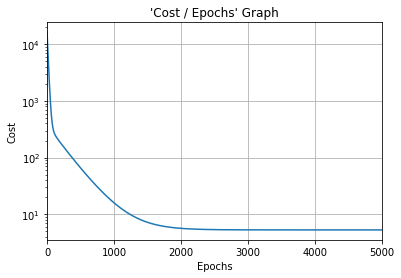
#for surface
x_range = np.arange(0,1,0.01)
y_range = np.arange(0,1,0.01)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x_range, y_range)
Z = X*W[0,0] + Y*W[1,0] + B
#plotting
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111,projection = '3d')
ax.scatter(x_input[:,0], x_input[:,1], labels, c = 'red', marker = 'o', alpha = 0.5)
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, alpha = 0.5)
ax.set_xlabel('scaled Age')
ax.set_ylabel('scaled BMI')
ax.set_zlabel('Blood Pressure')
plt.title('Data and Regression surface')
plt.show()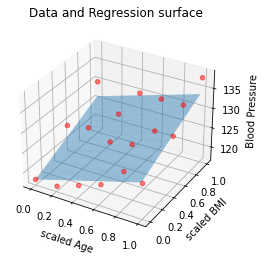
numpy)
age : 29
BMI : 25
blood pressure : 121.814mmHg
tensorflow)
age : 29
BMI : 25
blood pressure : 123.814mmHg
| Numpy | Tensorflow | |
| 변수 | 일반 변수 선언 | training 할 변수는 tf.variable() 상수는 tf.constant() |
| 구현 | np.mean(), *, + | tf.reduce_mean() tf.square() |
| 학습 | 직접 구현 | optimizer, minimize 사용 |
728x90
'Machine Learning' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Supervised Learning - Logistic Regression (multi-variable 2) (0) | 2023.08.06 |
|---|---|
| Supervised Learning - Logistic Regression (multi-variable 1) (0) | 2023.08.05 |
| Supervised Learning - Linear Regression (multi-variable 2) (0) | 2023.08.05 |
| Supervised Learning - Linear Regression (single-variable) (0) | 2023.08.05 |
| Machine Learning 개요 (0) | 2023.08.05 |



